Corneal ulcers are a very common problem in dogs and cats, and can result in blindness and even the loss of an eye. Previously, deep corneal ulcers have generally required surgery to treat them. This, however, can lead to significant scarring and visual impairment. Surgery is also rather costly and always requires a general anaesthetic.
Corneal collagen cross-linking, known as CXL, is a technique which was developed in the human medical field for treatment of people with corneal disease. It has been adapted recently for veterinary use and is offered by the Ophthalmology Specialists at DWR to treat melting corneal ulcers in dogs and cats. The procedure offers a cost‐effective and safe alternative treatment for melting corneal ulcers. It is non-invasive, results in less corneal scarring and usually reduces the required frequency of application of eye drops.
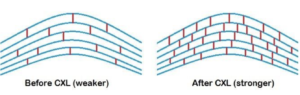
In dogs and cats, CXL may be performed conscious although sedation or general anaesthesia is sometimes needed. It involves serial application of riboflavin (Vitamin B2) eye drops to the surface of the eye which is then activated by illumination with ultraviolet light. The riboflavin absorbs the light and produces free radicals which cause new bonds (cross-links) to form between adjacent collagen strands in the stromal layer. This process increases biomechanical stability and strengthens the cornea. CXL can also sterilise the site of ulceration – killing off the bacteria which may be contributing to the melting process.
If you would like further information about corneal collagen cross-linking, or other ophthalmological procedures, please contact a member of our team: https://www.dickwhitereferrals.com/service/ophthalmology/